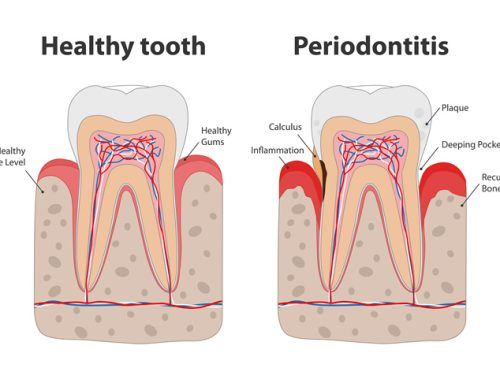
Periodontitis is a gum disease that is one of the most common oral problems among people. It occurs when the deeper periodontal structures and gums become inflamed. This inflammation causes gum bleeding, swelling, and redness. Inflammation is often caused by the accumulation of harmful bacteria around the teeth. It can spread to the roots of the teeth causing tooth decay, loosening of teeth, and even loss of teeth.
Periodontitis is a gum disease that is one of the most common oral problems among people. It occurs when the deeper periodontal structures and gums become inflamed. This inflammation causes gum bleeding, swelling, and redness. Inflammation is often caused by the accumulation of harmful bacteria around the teeth. It can spread to the roots of the teeth causing tooth decay, loosening of teeth, and even loss of teeth.
Symptoms and Signs
It is important to recognize the signs of Periodontitis to quickly treat the disease before it begins to affect overall oral health. Some of the symptoms of Periodontitis include:
- Persistent swelling in the gums
- Inflamed or swollen gums
- Red, or even purple, gums
- Gums recede causing teeth to look bigger
- Pain in gums upon touch
- Gaps between teeth and gums
- Bleeding gums during flossing or brushing teeth
- Persistent bad breath
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth or loss of teeth
Risk Factors
Weakened immune systems and high level of bacteria in the mouth can cause gum disease. Some bad habits can increase the likelihood of Periodontitis.
- Smoking can weaken the immune system. Tobacco also has up to 28 cancer-causing agents that can result in gum problems
- Hormonal changes during puberty, menopause, and pregnancy can increase the risk of gum diseases
- AIDS can increase chances of gum disease due to a weakened immune system
- Diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease
- Cancer and cancer treatments can actually cause an increase in gum disease
- Different medications can cause a dry mouth, a weakened immune system, or dilated blood vessels. All of this can increase the chances of gum disease
- Genetic factors can increase the risk of gum disease in some people
Prevention
It is important to maintain good oral hygiene to reduce the chance of bacteria accumulation. To prevent infections teeth and gums need to be in their best condition. Dentists recommend brushing teeth at least twice in a day and flossing regularly. If there is some space between the teeth, an interdental brush needs to be used.
Dental checkups need to be kept regularly to clean out any plaque or calculus on the gums and teeth. Scaling can clean and remove debris from below the gum line. Bacteria that accumulate between the teeth and gums need to be cleaned properly.
Treatment
There are some medications that you can take to cure Periodontitis.
- An antimicrobial mouth rinse can reduce bacteria in the mouth
- Antiseptic chips are small gelatin pieces that are filled with antimicrobials like chlorhexidine
- Antibiotic gel shrinks periodontal pockets where bacteria usually form
- Antibiotic microspheres are placed in the pockets after root planning and scaling
- Enzyme suppressants prevent destructive enzymes which break down gum tissue from developing.
- Oral antibiotics can be taken orally and treat persistent periodontal infections
For more drastic cases, surgical intervention may be needed, which includes:
- Flap surgery reduces pocket sizes and removes deep rooted calculus.
- Bone and tissue grafts help regenerate gum tissue and bones that can become damaged from Periodontitis.
For more information, give HPS Dental a call. We can be reached at (248) 652-0024. We look forward to your call!