 Geographic tongue is a highly prevalent medical condition. But despite being a common condition, many people aren’t aware of this particular health problem. This condition currently affects between 1% and 3% of people globally. And while it can affect nearly anyone, it’s relatively more common among young adults. What’s more, it’s more common in females compared to their male counterparts.
Geographic tongue is a highly prevalent medical condition. But despite being a common condition, many people aren’t aware of this particular health problem. This condition currently affects between 1% and 3% of people globally. And while it can affect nearly anyone, it’s relatively more common among young adults. What’s more, it’s more common in females compared to their male counterparts.
So, what is a geographic tongue?
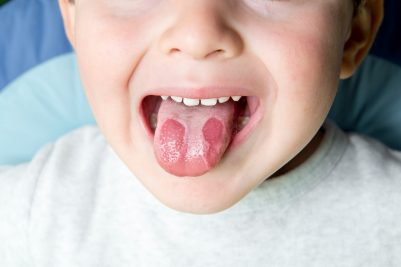
Just as the name implies, this condition derives its name from the uneven, smooth, red, or white patches that strikingly resemble a geographical map’s outline. It is worth noting that they may also develop in other areas of your mouth. Doctors may sometimes refer to it as erythema migrans or benign migratory glossitis.
Bearing in mind that geographic tongue is benign, it is neither harmful nor a serious medical condition that should warrant immediate medical intervention. What’s more, it is not contagious, implying that you won’t transmit it to another individual.
So, what causes this condition?
Geographic tongue occurs when your tongue’s old surface replaces itself. And while this might seem totally abnormal, it’s exactly what happens. Your tongue’s outermost layer fails to evenly come out. And in some areas, sections of the skin surface come away so soon that they leave behind a red and sore area that looks like a scratch on the affected skin. And in some instances, the skin stays on for an extended period, ultimately ending up looking like a white patch.
Because they are relatively thin, the red sections might become infected with candida, or thrush and will become sore as a result. Oral thrush is a very common condition that affects many people.
So, who is at risk of suffering from this condition?
As earlier explained, geographic tongue can affect nearly anyone, regardless of your gender, age, or anything else. What’s more, it is worth noting that this condition isn’t something one can transmit to those closest to them. However, it can potentially run in families. It is not an infection though.
So, what can acerbate your geographic tongue symptoms?
We have said that the symptoms of the geographic tongue are red, irregular patches. And while these symptoms will mostly appear on your tongue, they can also potentially appear on your gums, the top of your mouth, gums, or even below your tongue. These patches usually feature a white or light-colored border, and may also vary in color shape, or size.
And because the red patches are usually thin and fresh, they can be very painful when you consume foods rich in acids such as citrus fruits, or spicy foods such as pepper. However, these foods won’t aggravate your symptoms. Based on your feeding habits or lifestyle, you will identify the foods that make your symptoms more uncomfortable.
So, how is the condition diagnosed?
Usually, this condition is very easy to diagnose. In fact, your dental team can diagnose the condition just by looking at your mouth or tongue to be more specific.
So, what are my treatment options?
Currently, there is no treatment option for geographic tongue. Your doctor may recommend medications for oral thrush, such as miconazole gel to help alleviate your symptoms. Most importantly, it is important to reiterate that geographic tongue will never develop into cancer! But you will have to learn and know how to live with it. And this may involve identifying what foods worsen your symptoms, and avoiding them if possible. Of course, if your symptoms worsen, you should seek immediate medical attention.
If you are looking for a dentist, HPS Advanced Dental Care would love to see you. Dr. Heather is gladly accepting new patients.
We are located at 4741 24 Mile Rd. Shelby Township, MI 48316, and we can be reached at (248) 652-0024. We look forward to meeting you!





